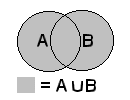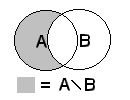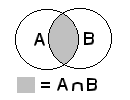Home
- POV-Ray Tutorials
POV-Ray Introduction
Content - INDEX
1. Working with POV-Ray:
"Insert Menu Add-on".
2. Basics on
How To Make a Scene.
3D Coordinates,
Floats and Vectors
3. Scene Structure
Basic example.
4. Scene File Header,
#include files,
camera, light_source.
5. Basic Geometric Objects
sphere, box, cylinder,
cone, torus, plane.
and other shapes
>6. Transformations
Streching, Turning,
Moving and others.
CSG: union,
difference, intersection.
7. Colors on Surfaces
texture, pigment, normal, finish
8. #declare, #local, #macro,
placeholders + flexible objects.
9. #while Loops
Basic examples.
10. #include, include files,
re-usable objects.
11. Efficiency,
speed, flexibility,
modulare working
adapting from 3.1 to 3.5;3.6
adapting from 3.5;3.6 to 3.7
POV-Ray + Windows Vista.
- Insert Menu Add-on
& Download
|
Transformations:
Scaling, Reflection, Rotation, Translation
For more details see "Geometric Transformations".
These transformations can be applied as well as on the geometrie of an object as on e.g. its texture or
on its texture components.
'scale' = scaling / resizing - enlarging or reducing in size -
The strechings are all defined relative to the center of the system of coordinates <0,0,0>.
Scaling causes a centric streching in the according direction of the coordinates.
Examples:
scale 2 causes the same as scale<2,2,2>: the size of the shape grows in
all directions twice.
scale 0.5 in all directions together multiplied by 0.5 - this means: all reduced to its half
scale<1.0,0.5,3.0> different sizing in x- ,y- and z-direction.
Here: in x-direction original - no change, in y-direction reduced to the half
and in z-direction increased to 3 times stretched.
scale<-1,1,1> Reflection at the yz-plane: This reflects an object at the yz-plane.
 Attention: scale <2,0,0> i.e. causes a
"Parse Warning: Illegal Value: Scale X by 0.0. Changed to 1.0."
Attention: scale <2,0,0> i.e. causes a
"Parse Warning: Illegal Value: Scale X by 0.0. Changed to 1.0."
Means: Changed to scale <2,1,1> because multiplying a component with zero does not make any sense!
'rotate' / turning around -
"rotate" causes a rotation according the "Left-thumb-rule" around the according axis
of the system of coordinates.
Example: rotate<0,45,0> turns a shape around the y-axis by 45 degrees.
 Attention:
The rotations are always defined relative to the axis of the system of coordinates!!
Attention:
The rotations are always defined relative to the axis of the system of coordinates!!
The rotations are not applied relative of any local axes of symmetry through the center of an object
but everytime relative to the axes of the coordinate system.
 Attention: The rotations will be applied in the written order!
Sequential rotations around different axes
are not commutative (interchangeable)!
Attention: The rotations will be applied in the written order!
Sequential rotations around different axes
are not commutative (interchangeable)!
'translate' = parallel moving relatively to a starting position.
"translate" causes a translation (a parallel moving) without affecting the shape of an object.
Example: translate <-2,1,3> moves the object by 2 steps to the left (-x-direction), by 1 step
upward (+y-direction) and by 3 steps ahead (+z-direction).
Other transformations:
By using the transformation matrix
it is possible to realize all the above mentioned transformations as well as
also much more complex affine transformations, e.g. shearing an object parallel
to a coordinate plane.
CSG (Constructiv Solid Geometry)
Boolean algebra with objects
Cut and paste and caving out by Boolean functions:
This is the most important technique of creating objects in 3D computer graphics!
1.: union = unification of objects = connecting different objects to a new object
(merge = used instead of union for transparent objects, if the inner borders are not wanted to be visible.
2.: difference = the rest of 1.object minus 2.object minus 3.object etc.
3.: intersection = this means those parts of all objects, which they have common with all of each other
| Connect it! |
Subtract it! |
What's in both? |
|
|
|
|
union{...}
oder merge{...} |
difference{...} |
intersection{...} |
|
|
|
|
 !!! Attention: The objects to be subtracted from another have to have no coincident surfaces.
It must reach unambiguous out of the first object.
In the case of coincident surfaces
the precision of computer calculation will be the trap: sometimes the surface is subtracted,
sometimes it is not - and this will happen in an very unpredictable manner!
(This error may occur only in some locations of the camera - but then it will be very very boring!)
!!! Attention: The objects to be subtracted from another have to have no coincident surfaces.
It must reach unambiguous out of the first object.
In the case of coincident surfaces
the precision of computer calculation will be the trap: sometimes the surface is subtracted,
sometimes it is not - and this will happen in an very unpredictable manner!
(This error may occur only in some locations of the camera - but then it will be very very boring!)
For details see: CSG - Constructiv Solid Geometry - Boolean Algebra with Solids.
|